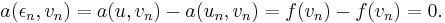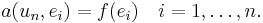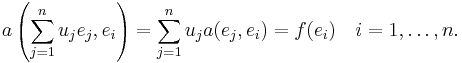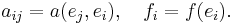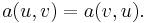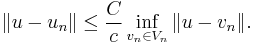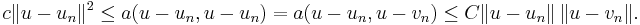Galerkin method
In mathematics, in the area of numerical analysis, Galerkin methods are a class of methods for converting a continuous operator problem (such as a differential equation) to a discrete problem. In principle, it is the equivalent of applying the method of variation of parameters to a function space, by converting the equation to a weak formulation. Typically one then applies some constraints on the function space to characterize the space with a finite set of basis functions. Often when using a Galerkin method one also gives the name along with typical approximation methods used, such as Petrov–Galerkin method (after Alexander G. Petrov) or Ritz–Galerkin method[1] (after Walther Ritz).
The approach is credited to the Russian mathematician Boris Galerkin.
Examples of Galerkin methods are:
- The Galerkin method of weighted residuals, the most common method of calculating the global stiffness matrix in the finite element method[2],[3]
- Boundary element method for solving integral equations
- Krylov subspace methods [4]
Contents |
Introduction with an abstract problem
A problem in weak formulation
Let us introduce Galerkin's method with an abstract problem posed as a weak formulation on a Hilbert space, 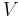 , namely,
, namely,
- find
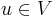 such that for all
such that for all 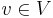 ,
, 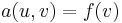 .
.
Here, 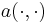 is a bilinear form (the exact requirements on
is a bilinear form (the exact requirements on 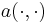 will be specified later) and
will be specified later) and  is a bounded linear functional on
is a bounded linear functional on 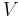 .
.
Galerkin discretization
Choose a subspace 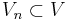 of dimension n and solve the projected problem:
of dimension n and solve the projected problem:
- Find
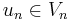 such that for all
such that for all 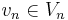 ,
, 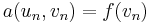 .
.
We call this the Galerkin equation. Notice that the equation has remained unchanged and only the spaces have changed.
Galerkin orthogonality
The key property of the Galerkin approach is that the error is orthogonal to the chosen subspaces. Since 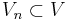 , we can use
, we can use 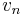 as a test vector in the original equation. Subtracting the two, we get the Galerkin orthogonality relation for the error,
as a test vector in the original equation. Subtracting the two, we get the Galerkin orthogonality relation for the error, 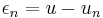 which is the error between the solution of the original problem,
which is the error between the solution of the original problem, 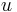 , and the solution of the Galerkin equation,
, and the solution of the Galerkin equation, 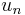
Matrix form
Since the aim of Galerkin's method is the production of a linear system of equations, we build its matrix form, which can be used to compute the solution by a computer program.
Let 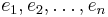 be a basis for
be a basis for 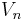 . Then, it is sufficient to use these in turn for testing the Galerkin equation, i.e.: find
. Then, it is sufficient to use these in turn for testing the Galerkin equation, i.e.: find 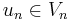 such that
such that
We expand 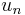 in respect to this basis,
in respect to this basis, 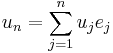 and insert it into the equation above, to obtain
and insert it into the equation above, to obtain
This previous equation is actually a linear system of equations 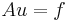 , where
, where
Symmetry of the matrix
Due to the definition of the matrix entries, the matrix of the Galerkin equation is symmetric if and only if the bilinear form 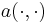 is symmetric.
is symmetric.
Analysis of Galerkin methods
Here, we will restrict ourselves to symmetric bilinear forms, that is
While this is not really a restriction of Galerkin methods, the application of the standard theory becomes much simpler. Furthermore, a Petrov-Galerkin method may be required in the nonsymmetric case.
The analysis of these methods proceeds in two steps. First, we will show that the Galerkin equation is a well-posed problem in the sense of Hadamard and therefore admits a unique solution. In the second step, we study the quality of approximation of the Galerkin solution 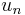 .
.
The analysis will mostly rest on two properties of the bilinear form, namely
- Boundedness: for all
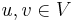 holds
holds
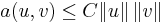 for some constant
for some constant 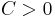
- Ellipticity: for all
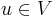 holds
holds
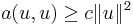 for some constant
for some constant 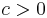
By the Lax-Milgram theorem (see weak formulation), these two conditions imply well-posedness of the original problem in weak formulation. All norms in the following sections will be norms for which the above inequalities hold (these norms are often called an energy norm).
Well-posedness of the Galerkin equation
Since 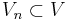 , boundedness and ellipticity of the bilinear form apply to
, boundedness and ellipticity of the bilinear form apply to 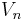 . Therefore, the well-posedness of the Galerkin problem is actually inherited from the well-posedness of the original problem.
. Therefore, the well-posedness of the Galerkin problem is actually inherited from the well-posedness of the original problem.
Quasi-best approximation (Céa's lemma)
The error 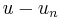 between the original and the Galerkin solution admits the estimate
between the original and the Galerkin solution admits the estimate
This means, that up to the constant 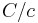 , the Galerkin solution
, the Galerkin solution 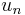 is as close to the original solution
is as close to the original solution 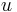 as any other vector in
as any other vector in 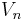 . In particular, it will be sufficient to study approximation by spaces
. In particular, it will be sufficient to study approximation by spaces 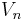 , completely forgetting about the equation being solved.
, completely forgetting about the equation being solved.
Proof
Since the proof is very simple and the basic principle behind all Galerkin methods, we include it here: by ellipticity and boundedness of the bilinear form (inequalities) and Galerkin orthogonality (equals sign in the middle), we have for arbitrary 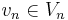 :
:
Dividing by 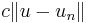 and taking the infimum over all possible
and taking the infimum over all possible 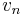 yields the lemma.
yields the lemma.
Application to the finite element method for Poisson's equation
Application to the analysis of the conjugate gradient method
References
- ^ A. Ern, J.L. Guermond, Theory and practice of finite elements, Springer, 2004, ISBN 0-3872-0574-8
- ^ S. Brenner, R. L. Scott, The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods, 2nd edition, Springer, 2005, ISBN 0-3879-5451-1
- ^ P. G. Ciarlet, The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems, North-Holland, 1978, ISBN 0-4448-5028-7
- ^ Y. Saad, Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems, 2nd edition, SIAM, 2003, ISBN 0-8987-1534-2
External links
|
|||||||||||